From Text to Code: How Digital NOTAMs Are Transforming Aviation Information
In the world of aviation, safety, timeliness, and accuracy of information are non-negotiable. One of the key tools used to disseminate time-sensitive information is the NOTAM (Notice to Air Missions). Traditionally, NOTAMs have been textual, manually interpreted messages that pilots and aviation stakeholders use to stay updated on changes in airspace, runway availability, hazards, and more. However, as aviation grows increasingly reliant on automation and digital systems, the need for a more structured, machine-readable form of NOTAM has led to the development of Digital NOTAM.
What is a Digital NOTAM?
A Digital NOTAM is a structured, data-centric representation of traditional NOTAM information designed to be read and processed automatically by computer systems. Unlike conventional NOTAMs, which are written in abbreviated, free-text format and require human interpretation, Digital NOTAMs provide a standardized, machine-interpretable format that can be directly integrated into modern aviation tools.
Digital NOTAMs are a part of the broader System Wide Information Management (SWIM) initiative promoted by aviation authorities like ICAO, FAA, and EUROCONTROL. This initiative aims to facilitate the seamless exchange of aeronautical, flight, and meteorological information for all aviation stakeholders.
The backbone of this system is the Aeronautical Information Exchange Model (AIXM), which provides the standardized language and structure for encoding this complex data.
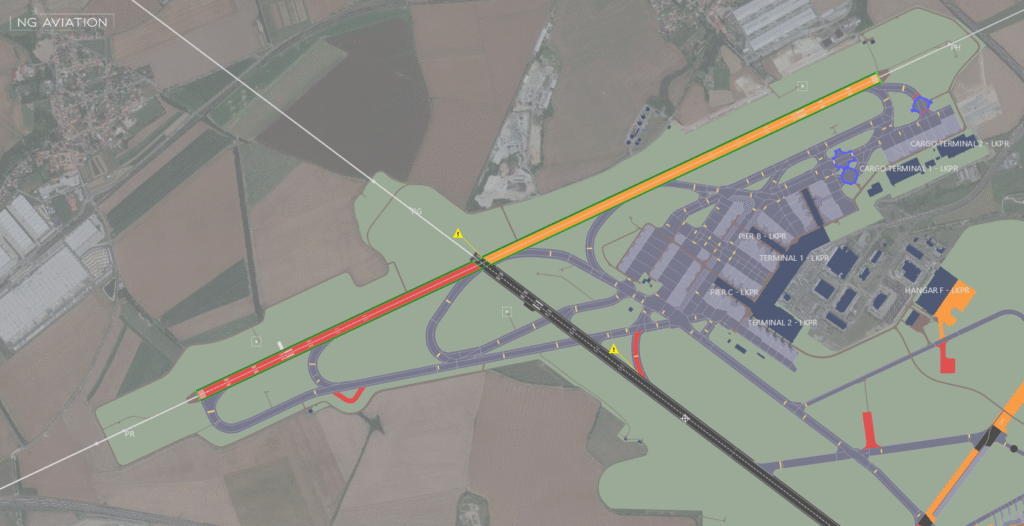
The Role of AIXM Versions
AIXM 5.1.1 – The Foundational Standard
The AIXM 5.1.1 is the most widely implemented version and serves as the current global standard for Digital NOTAMs. Its critical feature is a robust temporality model, which allows data to be tagged with specific start and end times of validity. This is the core function that enables a NOTAM’s temporary nature to be understood by a machine. This version provides the stable, proven framework for encoding events like runway closures, obstacle erections, and airspace activations.
AIXM 5.2 – The Next Evolution
Released in early 2025, AIXM 5.2 represents the next step in aeronautical data management. While not yet the primary standard for Digital NOTAMs, it introduces enhanced support for new technologies and procedures, such as complex GNSS operations and advanced runway condition reporting. The aviation industry is expected to migrate towards AIXM 5.2 as systems are updated progressively and the demand for more granular and complex data exchange grows.
How Digital NOTAMs are Visualized in an EFB
The most significant benefit for pilots is how Digital NOTAMs come to life in an Electronic Flight Bag (EFB). Instead of reading and interpreting lines of coded text, pilots can see critical information graphically.
Direct Map Overlays
- Airspace: Temporary Flight Restrictions (TFRs) and active Military Operations Areas (MOAs) are displayed as colored polygons, giving instant spatial awareness.
- Airport Diagrams: Closed runways or taxiways are overlaid with red markings or distinct symbols.
- Obstacles: Temporary cranes or towers appear as precise icons at their actual coordinates.
Color Coding and Filtering
- Status Indicators: Active NOTAMs are highlighted in red, while those scheduled soon may appear yellow or orange.
- Filtering Tools: Pilots can filter NOTAMs by route, altitude, or time window to focus only on mission-critical information.
Interactive Detail Layers
Each graphical element acts as a data gateway — tapping on it opens a pop-up window showing decoded details such as effective times, altitude limits, and radio frequencies.
This visual and interactive approach significantly reduces interpretation errors and enhances situational awareness.
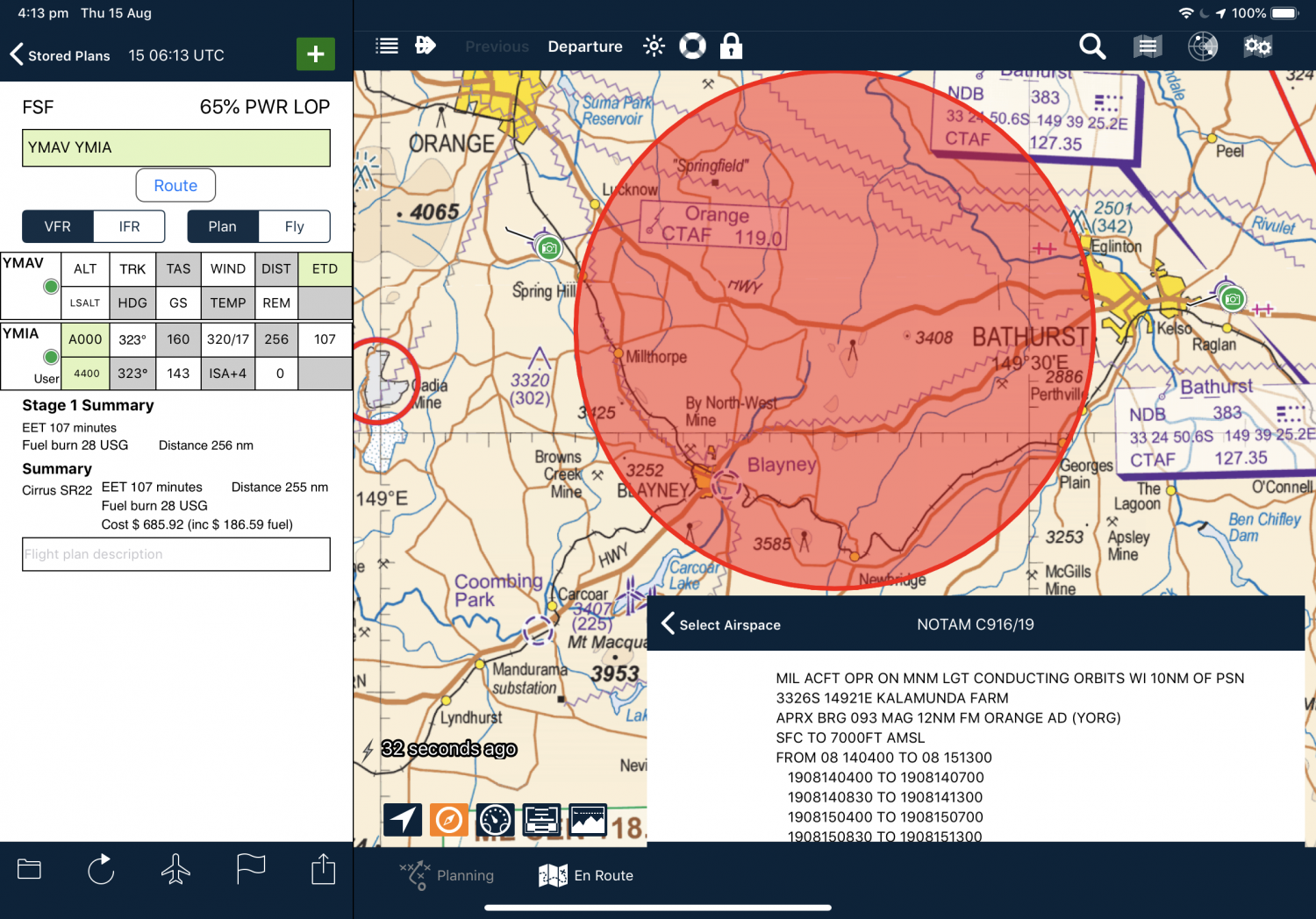
What about the Advantages and Challenges?
The transition to Digital NOTAMs brings massive benefits but also faces some challenges.
| Advantages | Challenges |
| Enhanced Accuracy – Standardized data removes ambiguity and minimizes human error. | Global Standardization – Requires worldwide adoption of common AIXM formats. |
| Improved Efficiency – Automatic filtering and visualization save pilots time during pre-flight. | Infrastructure Investment – Demands modernization of ground and onboard systems. |
| Seamless Integration – Enables unified data flow between cockpit, ATC, and airline systems. | Training & Human Factors – Personnel must adapt to and trust automated data sources. |
The Future is Digital
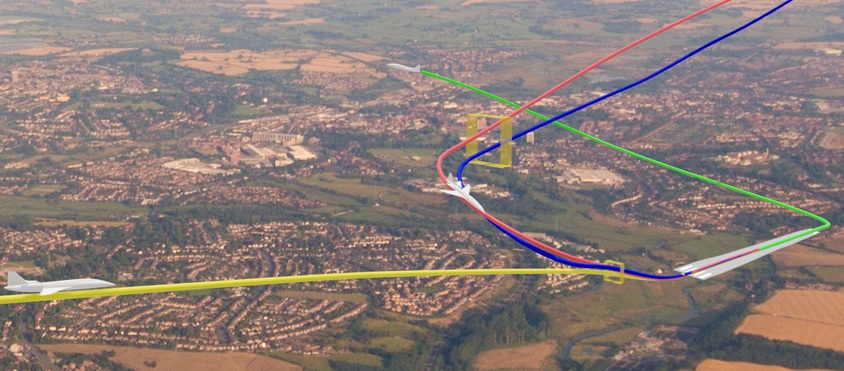
The implementation of Digital NOTAMs is a foundational step toward the next generation of Air Traffic Management (ATM). It is a key enabler for advanced concepts like 4D Trajectory Based Operations (TBO), which requires precise, machine-readable data to manage flight paths in three dimensions plus time.
Ultimately, the shift from ambiguous text to precise, structured data is a vital evolution. It is a critical move toward a safer, more efficient, and more connected future for global aviation.
All content published on this blog is the sole responsibility of the respective authors. The views and opinions expressed do not necessarily reflect those of the blog owner or the platform.
References
EUROCONTROL. (n.d.-a). Aeronautical Information Exchange Model (AIXM). Retrieved September 15, 2025, from https://www.eurocontrol.int/model/aeronautical-information-exchange-model
EUROCONTROL. (n.d.-b). Digital NOTAM. AIXM Aero. Retrieved September 15, 2025, from https://aixm.aero/page/digital-notam
EUROCONTROL. (2021, April). System Wide Information Management. Retrieved September 15, 2025, from https://www.eurocontrol.int/archive_download/all/node/12899
EUROCONTROL. (2025, February 14). AIXM 5.2 release. AIXM Aero. Retrieved September 15, 2025, from https://aixm.aero/page/aixm-52
Federal Aviation Administration. (n.d.). Aeronautical Information Exchange Model (AIXM). Retrieved September 15, 2025, from https://www.faa.gov/about/office_org/headquarters_offices/ato/service_units/mission_support/aixm
Federal Aviation Administration. (2021, October). NOTAM Modernization Summit – Session 2: Implementing ICAO Standards. Retrieved from https://www.faa.gov/sites/faa.gov/files/2021-10/NOTAM%20Mod%20Summit%20-%20Session%202%20-%20Implementing%20ICAO%20Standards.pdf
ForeFlight. (2024). Graphical NOTAMs in ForeFlight Mobile. ForeFlight Support. Retrieved September 15, 2025, from https://support.foreflight.com/hc/en-us/articles/6528754716567-What-do-the-graphical-NOTAM-colors-represent
International Civil Aviation Organization. (n.d.). iPack NOTAM Improvement. Retrieved September 15, 2025, from https://www.icao.int/CDI/notam-improvement
Kryvoruchko, O., & Zaliskyi, M. (2022). Impact of NOTAM on security and efficiency performance of flights (overview). Civil Aviation High Technologies, 25(1), 21-34. https://doi.org/10.26467/2079-0619-2022-25-1-21-34R-SYS. (2025, September 4). Digital NOTAM – The Future of Aeronautical Information. https://r-sys.eu/digital-notam-the-future-of-aeronautical-information/
Monteiro, L. B., Ribeiro, V. F., Garcia, C. P., Rocha Filho, G. P., & Li, W. (2023). 4D trajectory conflict detection and resolution using decision tree pruning method. IEEE Latin America Transactions, 21(2), 277–287. https://doi.org/10.1109/TLA.2023.10015220
Pictures: EUROCONTROL, AvPlan EFB, ResearchGate








Definitely one of the best explanations out there.
Moving from textual NOTAMs to digital formats sounds like a significant step forward for aviation safety – manually interpreting those messages can be prone to error. I found a helpful overview of related AI applications in data processing at https://seed3d.ai, which makes me wonder how quickly this transition will happen across the industry.
Lovely just what I was looking for.